Wondering what your blood oxygen saturation level is—and how you can measure it? Let’s go through a series of basic Q&As about this vital sign.
Originally published in 2014, this article on blood oxygen has been expanded and now includes pictures of ScanWatch, an innovation featuring SP02 measurement that was announced at CES 2020.
What is pulse oximetry?
Pulse oximetry is a noninvasive method that enables the measurement of a person’s blood oxygen saturation, which is often referred to as SpO2 or even “The Fifth Vital Sign” (the first 4 being your pulse, temperature, blood pressure and respiratory rate).
What is SpO2, a.k.a. blood oxygen saturation?
It is a percentage that reflects the level of oxygen available in your blood.
Why do doctors use it?
Pulse oximetry is a method doctors use for rapid assessment and monitoring of a patient’s respiratory function. It is also used to determine which patients might be suffering from hypoxia (a condition meaning the blood oxygen level is too low) and should take additional tests.
Why is it problematic not to have enough oxygen in the blood?
A low level of oxygen in the blood is generally a sign of respiratory failure. The heart and brain are organs that require a lot of oxygen to function, and they are the first to suffer from this pathology, which can sometimes have serious consequences.
“Everybody can benefit from tracking their SpO2 themselves”
Self-tracking SpO2 is now a reality, and can benefit many people
Until recently doctors were the only ones to use pulse oximeters, generally in a clinical setting. But as these tools are now more common, self-tracking your SpO2 has become a reality.
In fact, everybody can benefit from tracking their SpO2 themselves. Being healthy doesn’t mean that you won’t benefit from a preventive tracking of respiratory problems—checking your blood oxygenation can provide you with an early warning sign (plus you’ll have a history of measurements to show your doctor, which they are likely to welcome).
Oxygen saturation rate decreases with altitude
If you are a mountaineering fan or an athlete training at high altitudes to boost your endurance, measuring your oxygen saturation rate is very important as it can highlight potentially life-threatening hypoxic conditions.
An important measurement to follow pathologies
This easy-to-use method is also great for people with a variety of chronic conditions, including asthma and COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease), as it allows them to quickly assess the severity of their condition.
Oximetry also allows patients undergoing oxygen therapy to adjust the flow rate of their oxygen cylinders and offer regular and accurate measurements to their doctors.
“ScanWatch includes an optical sensor that uses photoplethysmography (PPG) technology.”
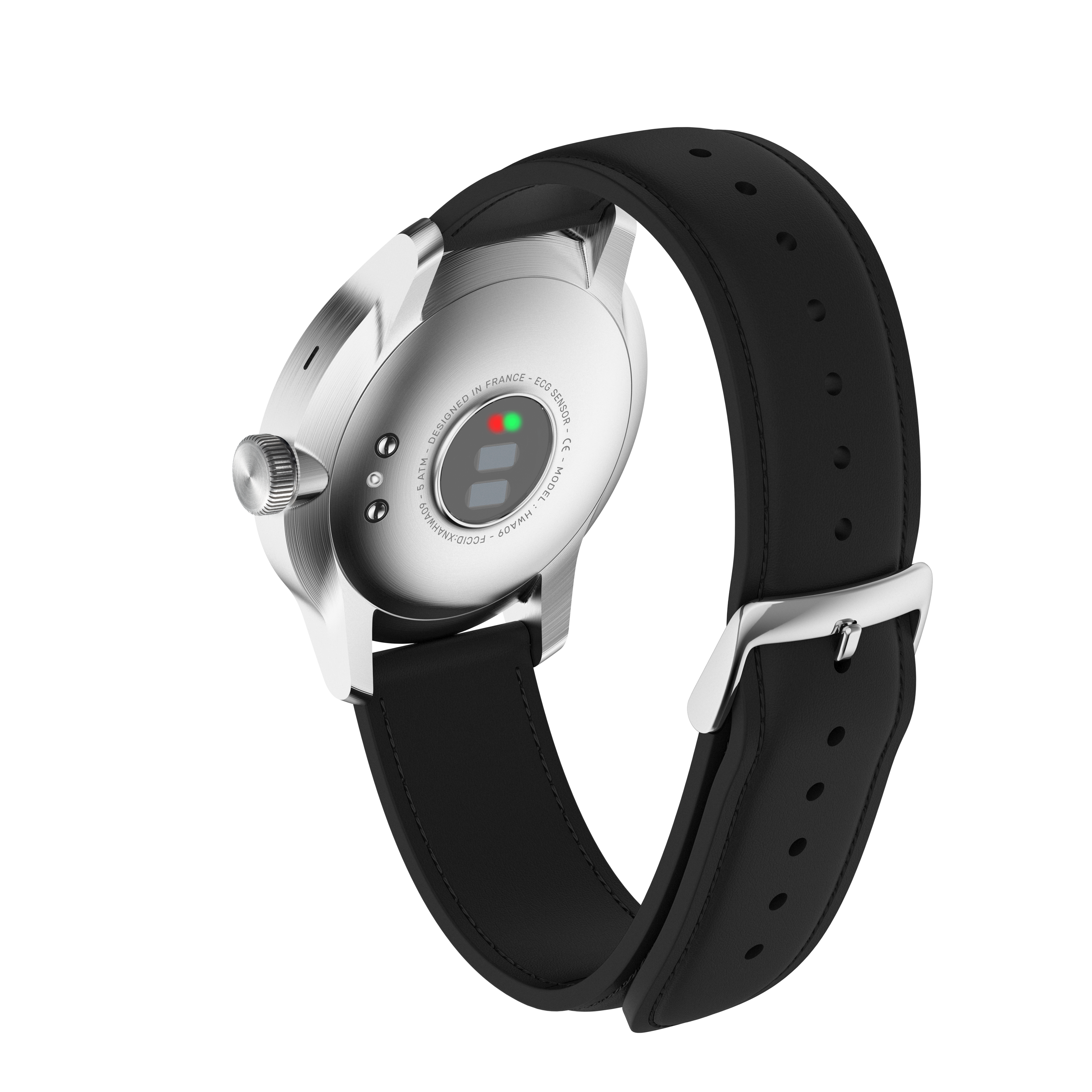

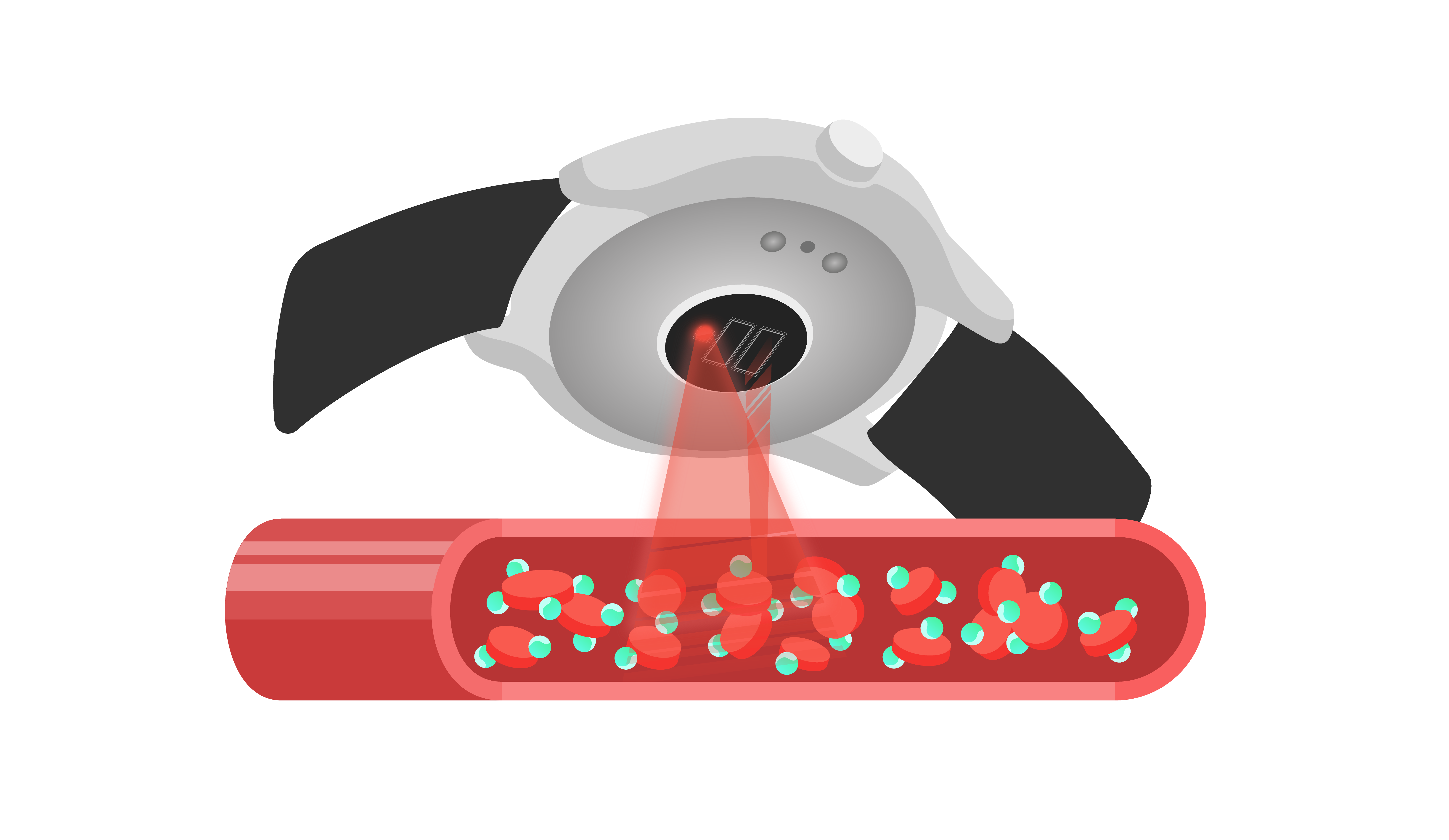
How does ScanWatch measure blood oxygen levels?
ScanWatch is a real watch and also an activity and sleep tracker with ECG functionality. But it also offers blood oxygen as a metric. The ScanWatch SpO2 sensor is located under the body of the watch. It uses the principle of reflection. It emits and then absorbs a red light wave which it sends through the blood vessels in order to analyze the oxygen saturation in the user’s blood. ScanWatch has an optical sensor that uses photoplethysmography (PPG) technology. It is based on an elementary principle: blood is red because it reflects red light. ScanWatch therefore uses red and infrared LEDs as well as light-sensitive photodiodes to detect the oxygen saturation in the blood of the veins crossing the wrist. A red LED and an infrared LED light up and radiate through your wrist. The ratio of red to infrared light passing through the ScanWatch photodiode indicates the percentage of oxygenated hemoglobin compared to the deoxygenated hemoglobin in your blood. This oxygen saturation in the blood is also called SpO2.
How should SpO2 readings be interpreted?
Oxygen saturation (SpO2) is an estimate of the amount of oxygen in your blood. It is given as a percentage of the maximum oxygen it can carry. Your SpO2 is considered normal if it is greater than 95%. If it is 95% or less, your blood has an abnormally low oxygen level and we recommend that you speak to your doctor. If the SpO2 is below 90%, the individual is at risk of developing hypoxemia. Symptoms may include shortness of breath, especially during brief exercise or even at rest.
When should I measure my SpO2?
You can measure your blood oxygen level at rest.
That’s it!
Hopefully this list of SpO2-related frequently asked questions has quenched your thirst for knowledge about your blood oxygen level. But if you have concerns about your own SpO2, it is always a good idea to consult with a health professional.